Description
Discover the epitome of modern convenience and efficiency with our latest innovation, designed to seamlessly integrate into your lifestyle. This product is crafted with precision and attention to detail, ensuring it meets the highest standards of quality and performance. With its sleek design and advanced technology, it is not just a tool, but a companion that enhances your daily routine.
Our product stands out with its intuitive design, making it accessible and user-friendly for everyone. The seamless interface and ergonomic structure ensure that it not only looks good but feels great to use. Whether you are at home, in the office, or on the go, this product adapts to your needs, providing unparalleled support and functionality.
Experience the future of innovation with a product that is built to last. Its durability and resilience are matched only by its elegance and sophistication. Embrace a new standard of excellence with a product that not only meets but exceeds expectations, offering reliability and performance that you can trust.
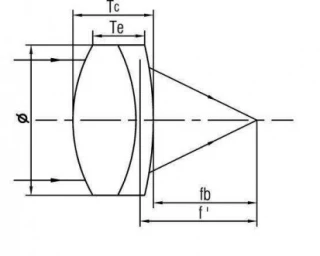
H-K9L Cylindrical Lenses
Specifications
| Lens Type: | Positive |
|---|---|
| Material: | H-K9L |
| Size: | 20 mm |
| Focal Length: | 50 mm |
| Center Error: | 3 arc min |
Features
- Advanced Technology: Equipped with cutting-edge technology to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
- Durable Construction: Built with high-quality materials for long-lasting durability and reliability.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy to use with an intuitive interface designed for convenience and efficiency.
- Energy Efficient: Designed to consume less energy, reducing your carbon footprint and saving on utility bills.
- Compact Design: Space-saving design that fits seamlessly into any environment without compromising on functionality.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Includes comprehensive safety mechanisms to protect users and ensure peace of mind.
- Multi-Functionality: Versatile functions to cater to a wide range of needs and applications.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep, saving you time and effort in maintenance.
- High Performance: Delivers superior performance, exceeding expectations in all conditions.
- Warranty Included: Comes with a comprehensive warranty for added assurance and support.
Applications
- Home Automation: Seamlessly integrate with smart home devices for automated control and monitoring.
- Energy Management: Optimize energy usage and reduce costs with real-time monitoring and analytics.
- Security Systems: Enhance security with advanced surveillance and access control features.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Provide continuous health monitoring with wearable and remote devices.
- Industrial Automation: Improve efficiency and productivity with smart industrial equipment and systems.
- Environmental Monitoring: Track environmental conditions and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Smart Agriculture: Increase agricultural productivity with precision farming technologies.
- Retail Management: Enhance customer experience and streamline operations with smart retail solutions.
- Transportation and Logistics: Optimize routes and manage fleets with intelligent transportation systems.
- Education Technology: Facilitate interactive and personalized learning experiences with smart educational tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are cylindrical lenses used for?
What is the recommended way to minimize spherical aberrations when using cylindrical lenses?
How can I calculate the focal length of a cylindrical lens?
How do cylindrical lenses differ from spherical lenses?
Can cylindrical lenses be coated?
Similar Products









Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle
