Description
The 1550nm Faraday Mirror is a passive optical component designed to rotate the polarization state of light by 45° or 90°, depending on the configuration. It utilizes the Faraday effect, achieved through a bismuth iron garnet (BIG) crystal placed in a magnetic field, to induce non-reciprocal polarization rotation. This device is essential for applications requiring precise polarization control, such as fiber optic networks, interferometric sensors, and fiber lasers. Its epoxy-free optical path ensures low insertion loss, high return loss, and robust temperature stability, making it suitable for demanding environments.
Applications include eliminating polarization induced fluctuations in fiber interferometers, Brillouin amplifier systems, fiber laser systems, and fiber optic antenna remoting systems. Our Faraday Mirror is optical path epoxy free and thus offers low insertion loss and high temperature stability.
1550nm Faraday Mirror
Specifications
| Center Wavelength: | 1550 nm |
|---|---|
| Operating Bandwidth: | 30 nm |
| Insertion Loss (max): | 0.6 dB |
| Faraday Rotation Angle (single Pass): | 45 deg deg |
| Center Wavelength: | 1550 nm |
| Faraday Rotation Angle: | 45° |
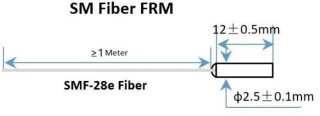
| Dimensions: | Ø5.5mmxL35mm |
| Pigtails Diameter: | 900μm Loose Fiber |
| Fiber Length: | 1.0m |
| Connector: | None |
Features
- High isolation to minimize polarization-related fluctuations.
- Low insertion loss, typically around 0.6 dB, ensuring efficient signal transmission.
- High return loss, enhancing signal integrity by reducing reflections.
- Compact size (Ø5.5mm x L35mm) for easy integration into various systems.
- Epoxy-free optical path, contributing to low insertion loss and superior temperature stability.
- Capable of handling optical power up to 500mW.
- Operates within a temperature range of -5°C to +70°C, suitable for various environmental conditions.
Applications
- Fiber optic amplifiers, ensuring consistent polarization and minimizing noise.
- Fiber optic systems testing, providing stable polarization for accurate measurements.
- Fiber optic LAN systems, maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
- Telecommunications, reducing polarization-induced fluctuations for reliable data transmission.
- Fiber interferometers, enhancing stability by eliminating polarization sensitivity.
- Brillouin amplifier systems, improving performance by controlling polarization.
- Fiber laser systems, ensuring consistent output by managing polarization.
- Fiber optic antenna remoting systems, maintaining signal quality over extended distances.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the 1550nm Faraday Mirror?
What are the applications of the 1550nm Faraday Mirror?
What are the key features of the 1550nm Faraday Mirror?
What are the dimensions of the 1550nm Faraday Mirror package?
Can the Faraday Mirror be customized?
What is the operating wavelength and bandwidth of this device?
Can the 1550nm Faraday Mirror be used in high-power applications?
How does the Faraday Mirror perform in varying temperatures?
What is the typical application of this mirror in telecommunications?
Similar Products







Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle

