Description
The 1950nm Faraday Mirror is a sophisticated optical component designed to manage polarization in fiber optic systems. It operates by rotating the polarization plane of light passing through it, offering precise 45° or 90° polarization rotation. This passive device is critical for systems that demand high polarization stability, such as fiber optic networks, fiber lasers, and high-performance measurement instruments. Its epoxy-free optical path ensures low insertion loss, high return loss, and robust temperature stability. Designed for use in demanding environments, it ensures long-term reliability and minimal signal degradation in fiber optic systems.
1950nm Faraday Mirror
Specifications
| Center Wavelength: | 1950 nm |
|---|---|
| Operating Bandwidth: | 30 nm |
| Insertion Loss (max): | 0.9 dB |
| Faraday Rotation Angle (single Pass): | 45 deg deg |
Features
- High isolation for reducing polarization fluctuations.
- Low insertion loss of 0.6 dB (typical) ensures minimal signal degradation.
- High return loss improves signal integrity and reduces reflection.
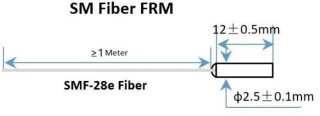
- Compact size (Ø5.5mm x L35mm) for easy integration into tight spaces.
- Epoxy-free optical path offers low insertion loss and superior temperature stability.
- Suitable for handling optical power up to 500mW.
- Designed for operation in temperatures ranging from -5°C to +70°C.
Applications
- Fiber optic amplifiers, ensuring polarization stability.
- Fiber optic systems testing to mitigate polarization-related issues.
- Fiber optic LAN systems for maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
- Telecommunications for stable data transmission with reduced polarization sensitivity.
- Fiber interferometers, to eliminate polarization fluctuations.
- Brillouin amplifier systems, enhancing performance.
- Fiber laser systems, ensuring consistent operation without polarization disruption.
- Fiber optic antenna remoting systems, improving signal reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main function of the 1950nm Faraday Mirror?
How does this Faraday Mirror help with polarization sensitivity?
What makes this Faraday Mirror ideal for high-precision systems?
What is the operating wavelength and bandwidth of this device?
Can the 1950nm Faraday Mirror be used in high-power applications?
How does the Faraday Mirror perform in varying temperatures?
What is the typical application of this mirror in telecommunications?
Similar Products







Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle

