Description
Nd:YAG Crystal is renowned as the premier choice among rare earth garnet materials, distinguished by its four-level system that facilitates low threshold operation in both pulsed and continuous wave (CW) modes. This crystal stands as the most mature and extensively utilized solid-state laser material, catering to a diverse clientele that includes research and development, medical, industrial, and military sectors. Its balanced properties offer an optimal compromise between the strengths and limitations of competing materials, making it a versatile component in various laser systems such as frequency-doubled continuous wave lasers and high-energy Q-switched pulse lasers.
Compared to other laser crystals, the Nd:YAG crystal boasts a fluorescence lifetime that is double that of Nd:YVO4, along with superior thermal conductivity. At LASERTEC, we specialize in the growth and fabrication of high-purity, low-loss rare-earth doped YAG laser materials. Our research endeavors have led to significant advancements, resulting in laser materials that exhibit enhanced efficiency, increased output power, improved damage resistance, reduced thermal lensing, higher brightness, and superior TEM00 output. We provide custom manufacturing solutions for laser rods, slabs, discs, passive q-switches, and YAG optics, catering to both high-volume production and low-volume development needs.
Our Nd:YAG crystals are crafted with precision, ensuring high optical quality and low loss at 1064 nm. They are designed for ease of operation in TEM00 mode, whether in Q-switch, pulsed, or CW applications. With excellent mechanical and thermal properties, these crystals are engineered to deliver high gain, high efficiency, and low threshold performance, making them a reliable choice for a wide range of laser applications.
NDYAG Laser Crystal
Specifications
| Type Of Crystal: | Nd:YAG |
|---|---|
| Crystal Diameter: | 2 mm |
| Crystal Length: | 0.1 mm |
| AR Coating: | Both sides |
Features
- High Gain, High Efficiency, Low Threshold: NdYAG crystals offer superior performance with high gain and efficiency, making them ideal for various laser applications.
- High Optical Quality and Low Loss at 1064 nm: These crystals ensure excellent optical quality with minimal loss, enhancing laser performance at 1064 nm.
- Good Mechanical and Thermal Properties: NdYAG crystals are known for their robust mechanical and thermal properties, ensuring durability and reliability in demanding environments.
- Easy Operation with TEM00 Mode: Compatible with Q-Switch, pulsed, and continuous wave (CW) modes, NdYAG crystals facilitate easy operation in TEM00 mode.
- Superior Fluorescence Lifetime: The fluorescence lifetime of NdYAG crystals is twice that of Nd:YVO4, providing extended operational life and efficiency.
- Enhanced Thermal Conductivity: Improved thermal conductivity compared to other laser crystals, reducing thermal lensing and enhancing performance.
- Custom Manufacturing Options: We offer custom manufacturing of laser rods, slabs, discs, passive q-switches, and YAG optics to meet specific production needs.
- Advanced Coating Options: Various coating options available, including AR@1064nm R<0.2%, AR@1064nm R<0.2% & HT@808nm T>95%, HR@1064nm R>99.8% & HT@808nm T>95%, and HR@1064nm R>99.8%.
- Precision Specifications: NdYAG crystals are manufactured with precise specifications, including orientation (<111> or <100> within 5°), dimensional tolerance (Diameter +/-0.1mm, Length +/-0.5mm), wavefront distortion (< λ/8 at 633nm per inch), and surface quality (20/10).
- Wide Range of Standard Products: Available in various sizes and doping levels to suit different applications, with part numbers ranging from NdYAG-4080 to NdYAG-127120.
Applications
- Medical Applications: NdYAG crystals are widely used in medical lasers for procedures such as laser eye surgery, skin resurfacing, and tattoo removal due to their high efficiency and precision.
- Industrial Applications: These crystals are essential in industrial laser systems for cutting, welding, and marking materials, offering high power and reliability.
- Military Applications: NdYAG lasers are utilized in military technology for range finding, target designation, and laser-guided munitions, benefiting from their robustness and high output power.
- Research and Development: In R&D, NdYAG crystals are used for developing new laser technologies and applications, thanks to their versatility and high optical quality.
- Scientific Applications: These crystals are employed in scientific research for spectroscopy and other experimental setups requiring precise and stable laser sources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is NdYAG crystal?
What are the advantages of using NdYAG crystals?
What applications are NdYAG crystals used for?
How does NdYAG compare to other laser crystals?
What specifications are available for NdYAG crystals?
What coating options are available for NdYAG crystals?
What are the standard product options for NdYAG crystals?
Similar Products
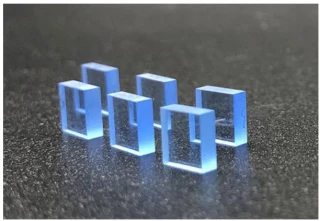


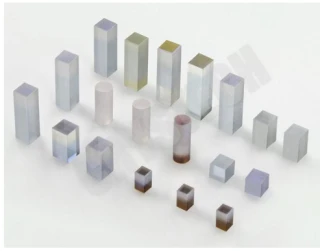

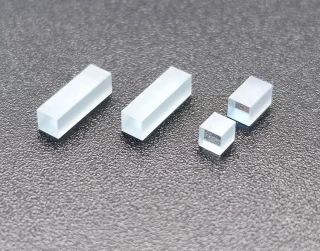


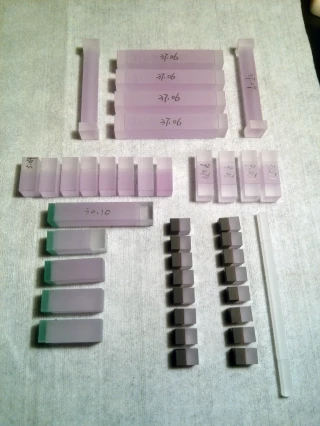


Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle

