Description
The Interspec 308 Portable FTIR Spectrometer is a state-of-the-art analytical instrument designed for precision and versatility in various spectroscopic applications. This compact and portable device offers exceptional performance, making it an ideal choice for both laboratory and field use. With its advanced technology, the Interspec 308 ensures accurate and reliable results, catering to the needs of professionals in diverse industries.
Engineered with a robust design, the Interspec 308 features a high-intensity air-cooled ceramic IR source and a multicoated KBr beamsplitter, providing excellent stability and efficiency. Its wide wavelength range, from 7000 to 400 cm-1 without the ATR accessory and 6000 to 600 cm-1 with the ZnSe ATR accessory, allows for comprehensive analysis across various samples. The spectrometer's resolution of 2 cm-1 ensures precise spectral data, making it a reliable tool for detailed material characterization.
Designed for user convenience, the Interspec 308 is equipped with a USB 2.0 interface and operates on a Windows-based software platform, facilitating seamless data acquisition and analysis. Its compact dimensions of W49xD39xH20 cm and lightweight design, weighing only 12 kg, make it easily transportable, enhancing its suitability for on-site measurements. The spectrometer's 18-bit high-speed data acquisition system further underscores its capability to deliver high-quality results swiftly and efficiently.
Manufactured by Interspectrum OU in Toravere, Estonia, the Interspec 308 Portable FTIR Spectrometer embodies cutting-edge technology and superior craftsmanship.
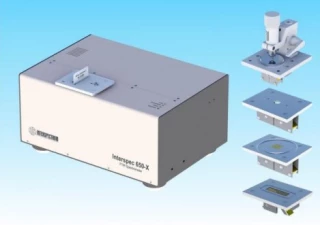
Portable FTIR Spectrometer Interspec 308
Specifications
| Standard Measurement Range: | 7000 – 400 cm-1 |
|---|---|
| Max Resolution: | 2 cm-1 |
| Wavelength Range (with ZnSe ATR Accessory): | 6000 to 600 cm-1 |
| Sample Handling: | 1 or 3 bounce ATR, transmission, reflection |
| Beamsplitter: | Multicoated KBr |
| Frequency Reference: | VCSEL laser |
| IR Source: | High intensity air cooled ceramic |
| Data Acquisition System: | 18 bit, high speed |
| Software: | Windows based |
| Interface: | USB 2.0 |
| Power: | 12 VDC, 30 W |
| Dimensions: | W49xD39xH20 cm |
| Weight: | 12 kg |
Features
- Wide Wavelength Range: 7000–400 cm⁻¹ (standard), 6000–600 cm⁻¹ (with ZnSe ATR accessory) for versatile analysis
- High Resolution: 2 cm⁻¹ ensures detailed spectral clarity
- Multiple Sample Handling Modes: 1 or 3 bounce ATR, transmission, and reflection for flexible use
- Multicoated KBr Beamsplitter: Enhances spectral performance and durability
- Stable Frequency Reference: VCSEL laser for accurate wavelength calibration
- High-Intensity IR Source: Air-cooled ceramic lamp for reliable signal strength
- Advanced Data Acquisition: 18-bit high-speed system for precise measurements
- User-Friendly Software: Windows-based with USB 2.0 interface for easy operation and data management
- Portable and Lightweight: Compact size and 12 kg weight facilitate fieldwork and transport
- Low Power Consumption: 12 VDC, 30 W power supply
Applications
- Pharmaceuticals: Analyze active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients for quality control and assurance.
- Environmental Monitoring: Detect pollutants and hazardous substances in air, water, and soil samples.
- Food and Beverage: Ensure quality and safety by analyzing ingredients, additives, and contaminants.
- Petrochemicals: Characterize crude oil, fuels, and lubricants for composition and purity.
- Polymers and Plastics: Identify polymer types and additives, and assess the degradation of materials.
- Academic Research: Support a wide range of spectroscopic studies in chemistry, physics, and materials science.
- Forensics: Analyze trace evidence, drugs, and explosives for criminal investigations.
- Art and Cultural Heritage: Study the composition and degradation of artworks and historical artifacts.
- Biotechnology: Investigate biomolecules and complex biological matrices for research and development.
- Agriculture: Assess soil health and crop quality by analyzing nutrients and contaminants.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the power source for the Interspec 308 spectrometer?
What is the resolution of the Interspec 308 spectrometer?
What is the wavelength range of the Interspec 308 spectrometer?
What is the weight and size of the Interspec 308 spectrometer?
What sample handling options are available with the Interspec 308 spectrometer?
Similar Products









Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle
