Description
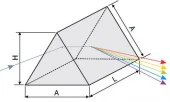
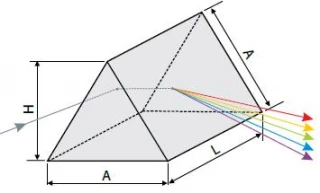
Dispersing Prisms are optical components designed to separate light by its wavelength. When a light ray passes through the prism, it is twice refracted, and the deviation is a function of the refractive index, which corresponds to the wavelength of the light.
These prisms are commonly used in applications requiring wavelength separation, such as spectroscopy, imaging, and other optical experiments. They are available in different materials, and dielectric coatings can be applied upon request for enhanced performance in specific spectral ranges.
14DP-2-1 Dispering Prisms
Specifications
| Material: | BK7 |
|---|---|
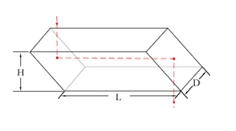
| Dimensions (A): | 25 mm |
| Dimensions (L): | 25 mm |
| Design Wavelength: | 800 nm |
| Thickness: | 10 mm |
| Surface Quality: | 40-20 scratch & dig |
| Flatness: | λ/4 @ 633 nm |
| Angle Tolerance: | ±2 arcmin |
| Maximum Input Beam Diameter: | 6.0 mm |
Features
- Separates light by wavelength for wavelength separation applications
- Twice refracts light passing through the prism to achieve dispersion
- Available in various materials: BK7, UVFS, and SF11
- Dielectric coatings can be applied upon request
- Side length ranging from 15 mm to 50 mm
- Angle of the apex: 59° to 69°
- High surface quality (40-20 scratch & dig) for precise optical performance
- Flatness: λ/4 @ 633 nm
- Angle tolerance: ±2 arcmin
- Design wavelength: 800 nm
- Coatings: None (please refer to Coatings Section for available options)
Applications
- Spectroscopy and wavelength analysis in scientific research
- Wavelength dispersion in optical imaging systems
- Separation and manipulation of different wavelength components in lasers
- Light dispersion experiments in educational and laboratory settings
- Optical testing and calibration of wavelength-sensitive devices
Frequently Asked Questions
What are dispersing prisms used for?
Dispersing prisms are used for wavelength separation applications.
How does a light ray pass through the prism?
A light ray is twice refracted passing through the prism.
What is the deviation of the light ray passing through the prism a function of?
The deviation is a function of refractive index, and hence wavelength.
What are the applications of dispersing prisms?
The applications of dispersing prisms include wavelength separation, pulse stretching/compression, time delay, and beam deflection.
Can the dispersing prisms work as retro-reflectors?
Yes, as long as acceptance angle limitations for TIR from the roof faces are not exceeded, the right angle prisms can serve as a retro reflector, turning beams back to the original direction.
Similar Products
Thank You!
Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle