Description
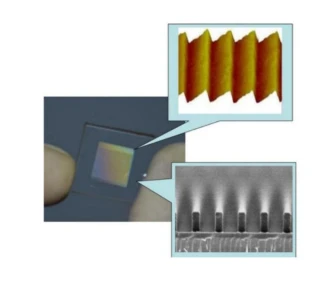
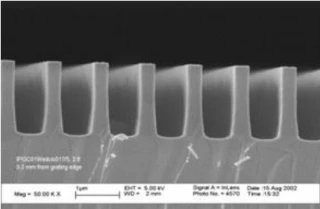
Holographic gratings are a type of diffraction grating that is created by exposing a polished negative to the interference of two laser beams, which forms fringes and creates a sinusoidal pattern on the exposure medium. This process is used to reduce or eliminate the effects of blazed gratings caused by periodic errors, such as ghost images or stray light. The holographic grating is less likely to produce a blaze and has a lower efficiency compared to the ruled grating. However, when the scribed width to wavelength ratio is close to 1, the efficiency of holographic gratings is virtually the same as that of scribed gratings.
Holographic gratings have a wide range of applications and are commonly used in spectrometers, spectrophotometers, and monochromators. This product is aluminized and has great reflectivity in the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared spectral ranges, making it an ideal choice for a variety of optical applications. Despite its lower efficiency, a holographic grating with 1800 lines per millimeter can be as efficient as a ruled grating at 500 nm. Customers can select holographic gratings based on their size, groove spacing, and blaze wavelength requirements.
Holographic Reflective Diffraction Gratings
Specifications
| Groove Density: | 600 l/mm |
|---|---|
| Spectral Range: | 250 – 500 nm |
| Blaze: | Not Blazed |
| Dimension (Length): | 12 mm |
| Dimension (Height): | 12 mm |
| Dimension (Thickness): | 6 mm |
| Substrate Material: | Custom |
| Dimension Tolerance: | ±0.5 mm |
| Clear Aperture: | ≥90% |
| Thickness: | 6.0 or 9.5 mm optional |
| Thickness Tolerance: | ±0.5 mm |
| Absolute Diffraction Efficiency: | 45%-65% |
| Groove Density: | 1200-2400 grooves/mm optional |
| Material: | Optical Glass |
| Coating: | Bare Aluminum |
Features
- Holographic Design: Utilizes holographic interference patterns to create finely detailed sinusoidal patterns, reducing or eliminating blazed grating effects such as ghost images and stray light, ensuring precise spectral dispersion.
- High Efficiency: While holographic gratings typically have lower efficiency compared to ruled gratings, they exhibit comparable efficiency when the ratio of scribed width to wavelength approaches 1. With an absolute diffraction efficiency ranging from 45% to 65%, these gratings offer excellent performance across various applications.
- Broad Spectral Range: Aluminized coating ensures exceptional reflectivity in the UV, visible, and IR spectral ranges, enabling accurate spectral analysis and dispersion.
- Dimensional Precision: Manufactured with dimension tolerances of ±0.5mm and a clear aperture of ≥90%, ensuring consistent optical performance and minimal light loss.
- Customizable Options: Available in multiple groove densities (1200-2400 grooves/mm) and dimensions (mm), providing flexibility to meet specific application requirements.
- Optional Thickness: Offered with optional thicknesses of 6.0mm or 9.5mm, catering to diverse experimental setups and optical systems.
- Durable Construction: Constructed from high-quality optical glass, ensuring durability and longevity in demanding laboratory environments.
- Bare Aluminum Coating: Coated with bare aluminum to maximize reflectivity and minimize light absorption, enhancing overall performance and efficiency.
Summary:
- Material: Optical Glass
- Dimension Tolerance: ±0.5mm
- Clear Aperture: ≥90%
- Thickness: 6.0mm or 9.5mm (optional)
- Thickness Tolerance: ±0.5mm
- Absolute Diffraction Efficiency: 45%-65%
- Groove Density: 1200-2400 grooves/mm (optional)
- Coating: Bare Aluminum
Applications
- Spectrometers and Spectrophotometers
- Monochromators and Optical Filters
- Laser Systems and Interferometers
- Analytical Instruments and Environmental Monitoring
- Astronomy and Astrophysics Research
Frequently Asked Questions
What are holographic gratings?
Holographic gratings are a type of diffraction grating that is created by exposing a polished negative to the interference of two laser beams, forming fringes and creating a sinusoidal pattern on the exposure medium.
What are the advantages of holographic gratings compared to ruled gratings?
Holographic gratings are less likely to produce a blaze and have a lower efficiency compared to ruled gratings. However, when the scribed width to wavelength ratio is close to 1, the efficiency of holographic gratings is virtually the same as that of scribed gratings.
What are the applications of holographic gratings?
Holographic gratings are commonly used in spectrometers, spectrophotometers, and monochromators.
What is the reflectivity range of the aluminized holographic gratings?
The aluminized holographic gratings have great reflectivity in the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared spectral ranges.
What factors can customers consider when selecting holographic gratings?
Customers can select holographic gratings based on their size, groove spacing, and blaze wavelength requirements.
Similar Products
Thank You!
Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle