Description
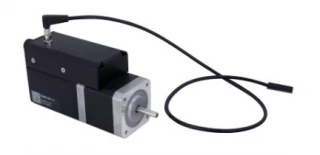
Experience a revolution in motion control with our NEMA 17 stepper motor, expertly designed with a built-in controller and motor encoder. This advanced motor is a standalone unit that requires only a standard 24 V or 48 V power supply, making it incredibly easy to integrate into your projects. The inclusion of a detachable home sensor, complete with a mounting screw and small magnet, ensures that you have everything you need for precise control right out of the box. For those who require additional functionality, an optional away sensor is also available.
Our NEMA 17 stepper motor is designed for versatility and ease of use. It features an indexed knob for manual control, allowing for flexible operation even when a computer is not available. The motor connects seamlessly to the USB 2.0 or RS-232 port of any computer, and can be effortlessly daisy-chained with other Zaber products. This daisy-chain capability is facilitated by convenient locking, 4-pin, M8 connectors that ensure secure connections between units. Additionally, the chain shares power, enabling multiple X-Series products to operate from a single power supply.
With up to 25,600 microsteps per revolution, this stepper motor offers precision and performance that are second to none. It can achieve speeds of up to 2,650 rpm with a maximum torque of 30 N·cm, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. The motor's robust design and compliance with RoHS and CE standards ensure reliability and peace of mind. Whether you're looking to simplify your motion control systems or enhance the capabilities of your current setup, our NEMA 17 stepper motor is the ideal choice.
Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-WE01
Specifications
| Microstep Size (default Resolution): | 490.866 urad |
|---|---|
| Accuracy (unidirectional): | 4.3625 mrad |
| Maximum Speed: | 2650.1 rpm |
| Minimum Speed: | 4607.592 urad/s |
| Integrated Controller: | Yes |
| Integrated Encoder: | Yes |
Features
- NEMA 17 Stepper Motor with Built-in Controller: Integrated controller and motor encoder for seamless operation.
- High Precision Microstepping: Achieve up to 25,600 microsteps per revolution for precise control.
- Impressive Speed and Torque: Capable of up to 2,650 rpm speed and 30 N·cm torque.
- Home Sensor Included: Comes with a detachable home sensor, mounting screw, and a small magnet; optional away sensor available.
- Daisy-chain Capability: Easily connect data and power with other X-series products for streamlined integration.
- Manual Control: Indexed knob provides convenient manual control without a computer.
- Versatile Connectivity: Connects via USB 2.0 or RS-232 port; supports Zaber ASCII and Zaber Binary communication protocols.
- Secure Connections: Features locking, 4-pin, M8 connectors for secure unit connections.
- Power Sharing: Multiple X-Series products can share a single power supply.
- High Accuracy and Repeatability: Unidirectional accuracy of 0.25° and repeatability of < 0.1°.
- Encoder Resolution: Motor-mounted rotary quadrature encoder with 500 CPR for high-resolution feedback.
- Robust Design: NEMA 17 motor frame size with a 5 mm shaft diameter.
- Compliance and Safety: RoHS and CE compliant, with operating temperature range of 0 to 50 °C.
- Compact and Lightweight: Weighs only 0.61 kg (1.345 lb).
Applications
- Precision Manufacturing: Ideal for use in CNC machines, 3D printers, and other precision manufacturing equipment where accurate motion control is critical.
- Robotics: Suitable for robotic arms and automated systems requiring precise and repeatable positioning.
- Laboratory Automation: Perfect for laboratory equipment that requires precise movement, such as automated microscopes or sample handling systems.
- Medical Devices: Can be used in medical equipment that demands precise and reliable motion control, such as imaging devices or surgical robots.
- Textile Machinery: Useful in textile machines where precise control of fabric movement is necessary.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Suitable for wafer handling and processing equipment that requires high precision.
- Optical Equipment: Ideal for use in optical inspection and manufacturing equipment where precise alignment is required.
- Automated Test Equipment: Can be used in testing systems that require precise and repeatable movement for accurate testing results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the maximum speed of the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-WE01?
Does the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-WE01 come with a home sensor?
Can the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-WE01 be used without a computer?
What is the power supply requirement for the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-WE01?
Can multiple X-Series products use a single power supply?
Similar Products
Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle