Description
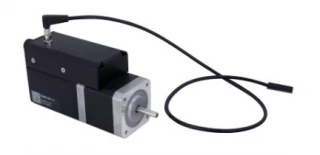
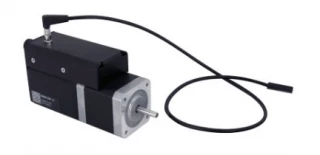
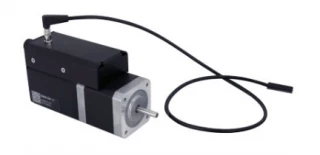
Experience the future of motion control with our NEMA 17 stepper motor, expertly designed with a built-in controller and motor encoder. This advanced motor simplifies complex tasks, offering an integrated solution that is perfect for a variety of applications. Its compact design includes a detachable home sensor, complete with a mounting screw and a small magnet, ensuring precise and reliable operation. Additionally, an optional away sensor can be incorporated to enhance its functionality. With its standalone capability, the motor operates efficiently with a standard 24 V or 48 V power supply, making it a versatile choice for any setup.
The NEMA 17 stepper motor is engineered for convenience and flexibility. An indexed knob allows for manual control, providing users with the ability to operate the motor seamlessly without the need for a computer. This feature is particularly beneficial in environments where quick adjustments are needed. The motor's connectivity options are robust, featuring compatibility with USB 2.0 or RS-232 ports, allowing it to be easily daisy-chained with other Zaber products. The secure, locking 4-pin M8 connectors ensure a stable and reliable connection, sharing power across multiple X-Series products with a single power supply.
Our stepper motor is a testament to precision and efficiency, capable of achieving up to 25,600 microsteps per revolution. It delivers impressive performance with speeds reaching up to 2,650 rpm and a torque of 30 N·cm. The motor's communication interface supports both Zaber ASCII and Zaber Binary protocols, ensuring seamless integration into existing systems. Built to meet rigorous standards, the motor is RoHS and CE compliant, offering assurance of quality and safety. With its innovative design and high-performance capabilities, the NEMA 17 stepper motor is the ideal choice for those seeking to simplify motion control in their projects.
Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-E01
Specifications
| Microstep Size (default Resolution): | 490.866 urad |
|---|---|
| Accuracy (unidirectional): | 4.3625 mrad |
| Maximum Speed: | 2650.1 rpm |
| Minimum Speed: | 4607.592 urad/s |
| Integrated Controller: | Yes |
| Integrated Encoder: | Yes |
Features
- NEMA 17 Stepper Motor with Built-in Controller: Offers integrated control for simplified motion management.
- High Precision Microstepping: Up to 25,600 microsteps per revolution for precise control.
- Impressive Speed and Torque: Achieves speeds up to 2,650 rpm and provides 30 N·cm torque.
- Included Accessories: Comes with a home sensor and small magnet; optional magnetic away sensor available.
- Versatile Connectivity: Daisy-chains data and power with X-series products for streamlined integration.
- Easy Manual Control: Indexed knob allows for manual adjustments without a computer.
- Flexible Communication Interfaces: Connects via USB 2.0 or RS-232, supporting Zaber ASCII and Binary protocols.
- Secure Connections: Features locking 4-pin M8 connectors for reliable unit connections.
- Compact and Compliant Design: NEMA 17 frame size with RoHS and CE compliance ensures quality and safety.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: Functions effectively from 0 to 50 °C.
- Power Efficient: Operates on a 24-48 VDC power supply with a maximum current draw of 1200 mA.
- Motor Specifications: 200 motor steps per revolution, 2-phase stepper motor with a rated current of 2300 mA/phase.
Applications
- Robotics: Ideal for precise control in robotic arms and automation systems.
- CNC Machines: Perfect for driving axes in CNC machining, ensuring high precision and repeatability.
- 3D Printing: Used to control the movement of print heads or platforms for accurate layer deposition.
- Laboratory Automation: Suitable for automating laboratory equipment, such as microscopes or sample handlers.
- Conveyor Systems: Provides controlled motion for conveyor belts in manufacturing and packaging lines.
- Camera Control: Enables precise positioning and movement of cameras in photography and film production.
- Medical Devices: Used in medical equipment for tasks requiring precise motion control, such as in surgical robots.
- Test and Measurement: Essential for applications that require exact positioning in testing and measurement setups.
- Textile Machinery: Applied in textile machines for accurate control of fabric movement and processing.
- Educational Purposes: Utilized in educational kits and projects to teach motion control and automation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the maximum speed of the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-E01?
What is the maximum torque of the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-E01?
Can the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-E01 be used without a computer?
What is the communication interface of the Stepper Motor X-NMS17C-E01?
Can multiple X-Series products be powered by a single power supply?
Similar Products
Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle