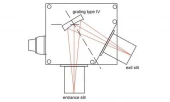
Description
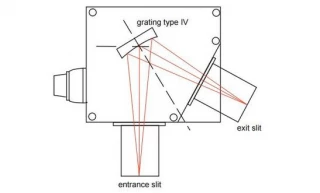
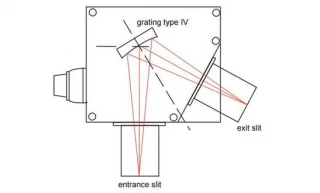
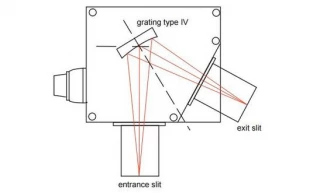
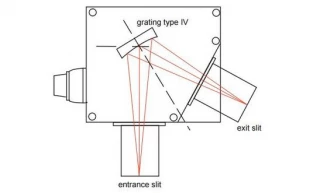
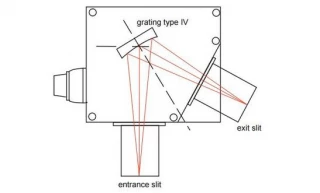
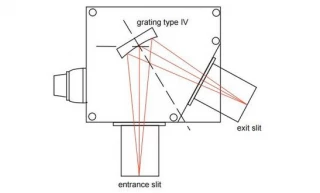
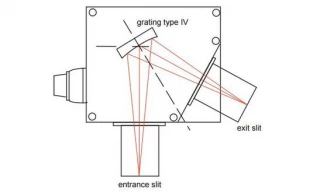
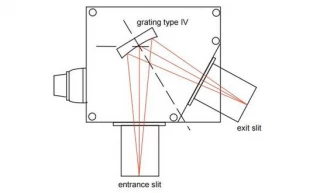
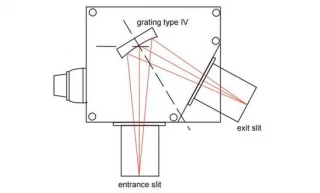
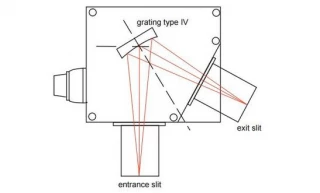
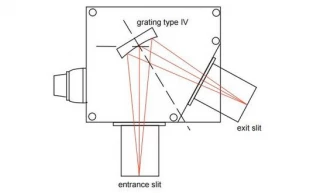
Using Type IV aberration-corrected monochromator Gratings, a single concave grating disperses, collimates and refocuses the light from the entrance slit onto the exit slit. Wavelength scanning is obtained through a simple rotation of the grating. The groove spacing of these gratings is computeroptimized to produce high quality images with a minimum
of astigmatism and coma, even at large numerical aperture. Compared with Czerny-Turner monochromators (equipped with one plane grating, one collimating mirror and one focusing mirror) Type IV aberration corrected monochromator gratings provide much better light collection efficiency and signal-to-noise ratio.
Monochromator Grating 522 00 600
Specifications
| Spectral Range: | 1000 – 2400 nm |
|---|---|
| Dispersion: | 9.6 nm/mm |
| Groove Density: | 500 l/mm |
| Deviation D: | 41.3 deg |
Features
In addition to the standard lists of Type IV flat field and monochromator gratings, HJY currently produces specific aberration-corrected concave gratings to maximize performance for a given application. In that case, using proprietary ray-tracing software, we optimize performance: resolution, throughput and signal to noise ratio. We need following data from our customers:
spectral range
configuration of use: monochromator or spectrograph
numeral aperture (F number) or size of grating
maximum overall dimension or maximum focal length
desired dispersion
desired resolution
entrance slit width and height or source geometry
minimum deviation: in general deviation has to be
minimum to improve correction of astigmatism, so indicate possible minimum deviation when overall dimensions of source, sample chamber and detector are taken into consideration.
at exit: if monochromator, exit slit width and height, and if flat field, length of detector, height and width of pixel.
Frequently Asked Questions
What data do you need from customers to optimize performance of a monochromator grating?
What is the commitment to quality for HORIBA Jobin Yvon's monochromator gratings?
How does a Type IV aberration-corrected monochromator grating differ from a Czerny-Turner monochromator?
What is the purpose of using specific aberration-corrected concave gratings?
What is a monochromator grating?
Similar Products

Your inquiry has been received.
Create an account by adding a password
Why create an account?
- Auto-complete inquiry forms
- View and manage all your past messages
- Save products to your favorites
- Close your account anytime — no hassle