The history of solar power, its milestones as well as its future: these topics are a staple in the discussion on renewable energy. In today’s blog post we will discuss specifically just how far solar power has come, briefly retracing solar cell history and milestones. We will focus on the breakthroughs that increased solar panel efficiency and see how far we have come since their invention.
The Beginning of Solar Cell History
To begin our tour of solar cell history and milestones let us pick our starting point. Solar energy has been used throughout millennia as a source of heat and, in turn as power. Consider a lens which can magnify the sun’s rays to start a fire. That said, in this discussion we will focus specifically on solar panels for electricity and their efficiency.
1800s
There were many preliminary discoveries which culminated in solar power being utilized. Notable scientists and findings include the following key milestones:
(1816) Robert Sterling created solar thermal electric technology to produce power
(1839) Edmond Becquerel discovered the photovoltaic effect
(1876) Willoughby Smith discovers the photoconductivity of selenium
In 1876 William Grylls Adams utilized Selenium’s ability to produce electricity when exposed to light. He wrote a book called “Solar heat: a substitute for fuel in tropical countries for heating steam boilers, and other purposes”. His book contains fundamental work on solar power. Future scientists utilized his work to continue developing solar power. This moment marked what we could call the beginning of direct sunlight to electricity conversion for power (albeit extremely limited).
(1883) A few years later in 1883, Charles Fritts invented the very first proper solar cell. This rudimentary cell was a thin layer of gold coated substrate with a thin layer of selenium. The resulting efficiency of the first solar cell was at about 1%.
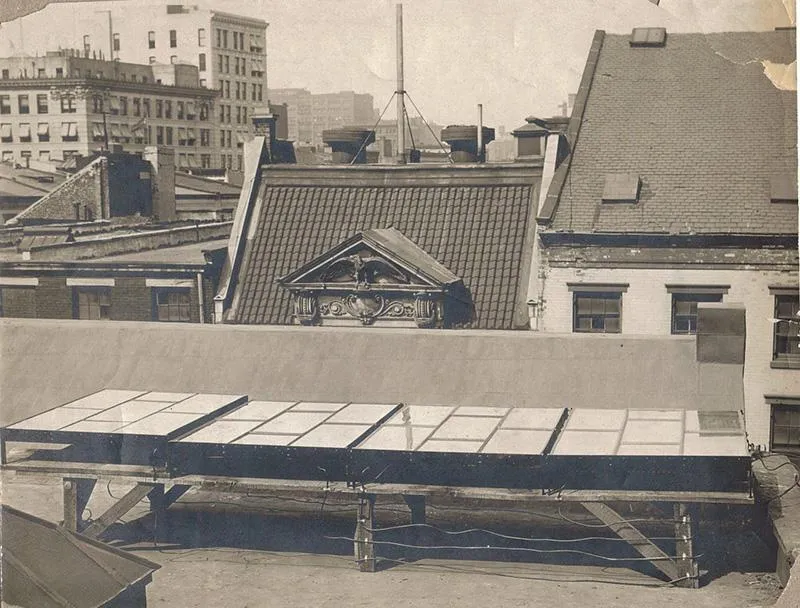

Charles Fritts installed his solar panels in 2884 on a New York City rooftop. image courtesy of smithsonianmag.com
(1888) Within the same decade in 1888, Edward Weston received U.S. Patent 389,124 and U.S. Patent 389,425 for solar cells.
Early – Mid 1900s
This century included even more discoveries and advancements which furthered human understanding of materials and the photoelectric effect. Solar cell history and milestones were certainly much more impactful in this century.
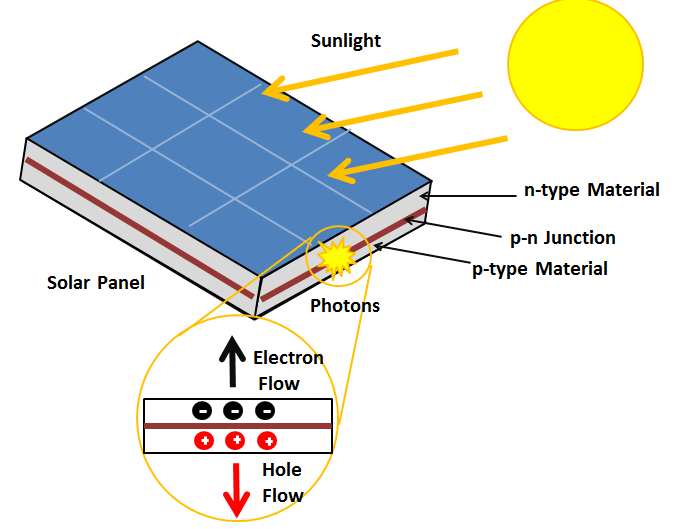
The Photovoltaic effect demonstrated in a solar panel as the process by which electricity is generated from sunlight. Image courtesy of energyeducation.ca
(1904) Wilhelm Hallwach discovers photosensitive combination of copper and cuprous oxide
(1905) Albert Einstein published a paper on the photoelectric effect
(1916) Robert Millikan provided experimental proof of photovoltaic effect
(1918) Jan Czochralski developed a method for growing single-crystal silicon
(1932) Audobert and Strora discover photoelectric effect in cadmium sulfide
(Mid-1900s) The mid 1900s introduced the solar era of solar cell history and milestones. 1954 marked the year photovoltaic technology was officially born. In the United states Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller and Gerald Pearson developed the Silicon PV cell at Bell Labs. This cell began with 4% efficiency which was later increased to 11%. From this point on solar cell and solar panel history exploded with discoveries and implementations. Further readings provide a much deeper look at these events.
Late 1900s
(1964-1966) Due to an increase in viability, solar power began to be utilized and researched much more seriously. Solar arrays were even included on the first Nimbus spacecraft (1964) and NASA’s first Orbiting Observatory (1966).
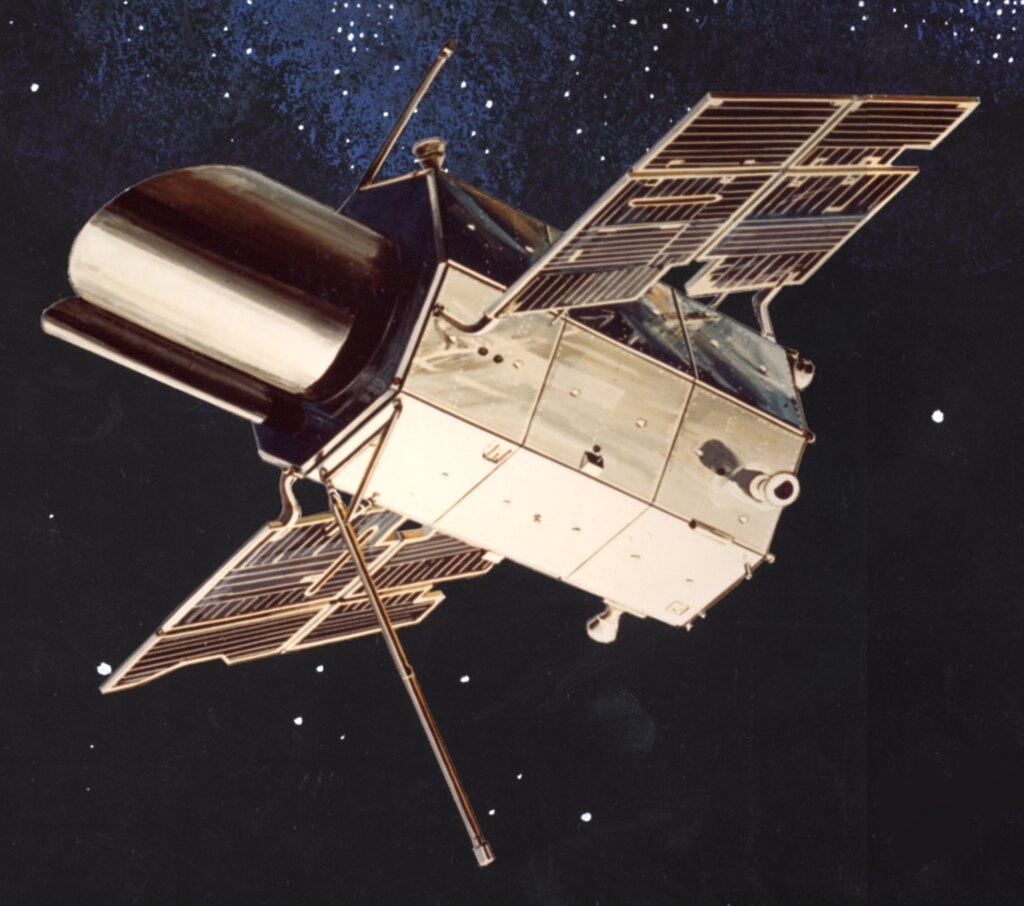

Artist rendition of OAO 1 in orbit, showing its inclusion of solar panels which were included in future OAO. Image courtesy of Wikipedia
(Early 1970s) In the 1970s Dr. Elliot Berman designs a much cheaper solar cell which reduced the price per watt down from $100/watt to $20/watt.
(1976) David Carlson and Christopher Wronski fabricate first amorphous silicon photovoltaic cells
(1977) U.S. Department of Energy launches Solar Research institute
(1980) University of Delaware develops first thin-film solar cell with over 10% efficiency using copper sulfide/cadmium sulfide
(1985) University of South Wales creates silicon solar cell with over 20% efficiency
(1992) University of South Florida develops 15.9% efficient thin-film cell made of cadmium telluride
(1994) The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) develops an over 30% efficiency solar cell made from gallium indium phosphide and gallium arsenide
(1999) National Renewable Energy Labs creates a thin-film cell with 18.8% efficiency
If you like this article, you might also interested in 5 Emerging Battery Technologies.
2000s
Today solar cells and solar panels have found a market on earth. Increasing efficiency with diminishing cost makes solar power all the more appealing. Consider the efficiency and capital cost over time graphs shown below. These grapes are specifically for Crystalline Silicon, Thin-Film Cells, and Concentrator cells.
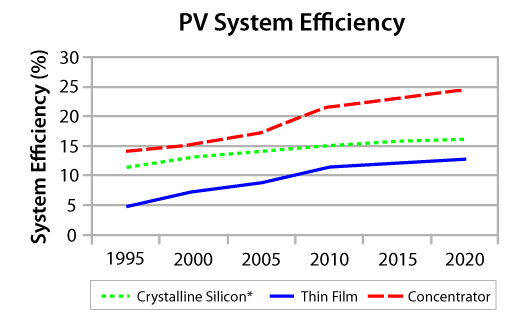
PV system efficiency from 1995 to 2020. image courtesy of Lafayette.edu
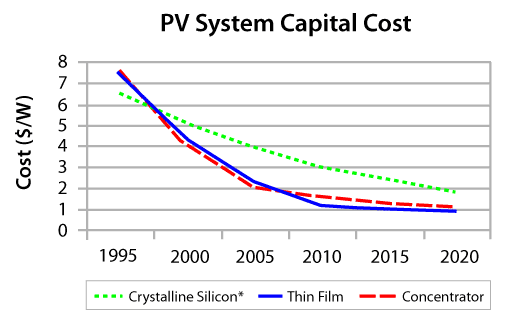
PV system capital cost from 1995 to 2020. Image courtesy of Lafayette.edu
The result of these trends resulted in solar array implementation in various locations. From NASA utilizing solar panels on virtually every craft sent to space to Home Depot selling residential solar power systems (2001). Government bodies such as NASDA began solar projects which used solar powered systems to begin transmitting power (2001).
By the 2010s prices had fallen by 70%, this brought solar power to finally be competitive with other forms of electricity generation.
(2011) U.S. DOE launched the SunShot Initiative which drove costs down significantly by 2017.
Private companies have begun developing their own private solar cells by the 2010s which are not on the market. These cells have reported incredible efficiencies reaching as high as 44%.
While research on solar cells has not stopped, the technology has advanced enough to be widely implemented worldwide.
Conclusion
It would appear that the growth of solar power is still ongoing. The solar cell industry is bigger in our time than it has ever been. The optimization of designs in conjunction with new material discoveries create the appealing trends seen in this article. Solar power history and milestones are fascinating and are rather inspiring. This is because it truly has been a worldwide endeavor with scientists’ works over two centuries culminating in one of the most renewable sources of energy on the planet.
We look at solar power with optimism for its future. Efficiency of solar panels on the market as of writing this article is at 22.8%. In addition to this the cost per watt is lower than ever. Remembering that the first cell in 1954 had an efficiency of about 1% shows just how far we have come.
Further Readings
There are many other very important events not touched in this shorter article. Additional sources in solar history and milestones are below to act as a starting point for interested readers.

Great article!